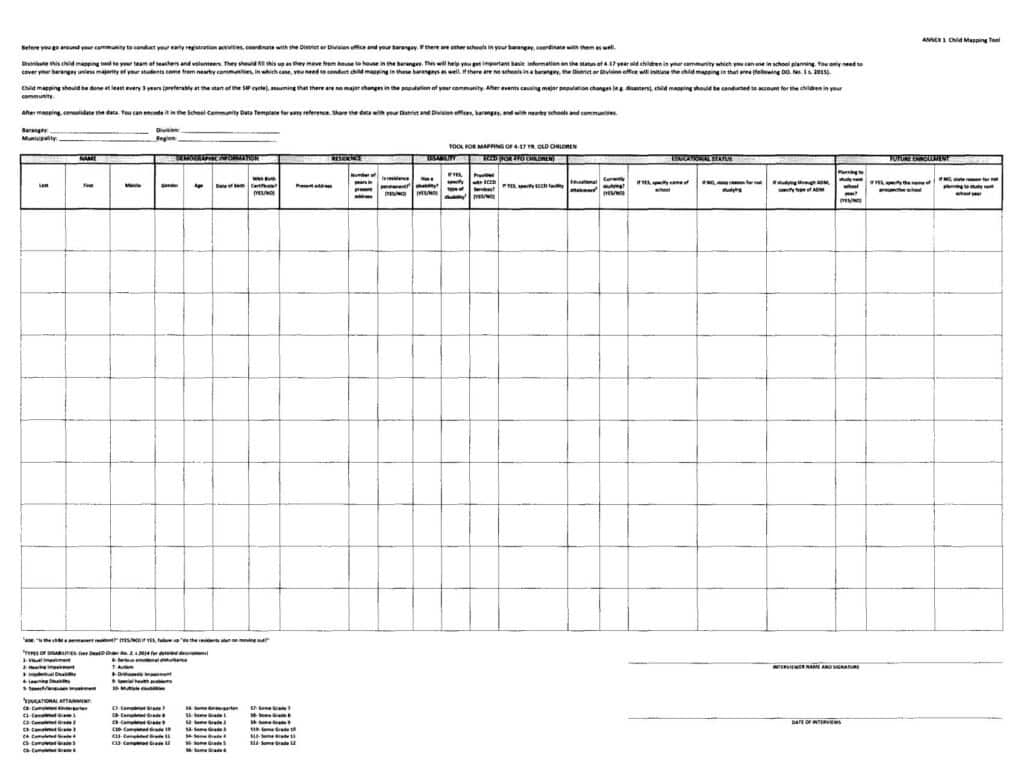
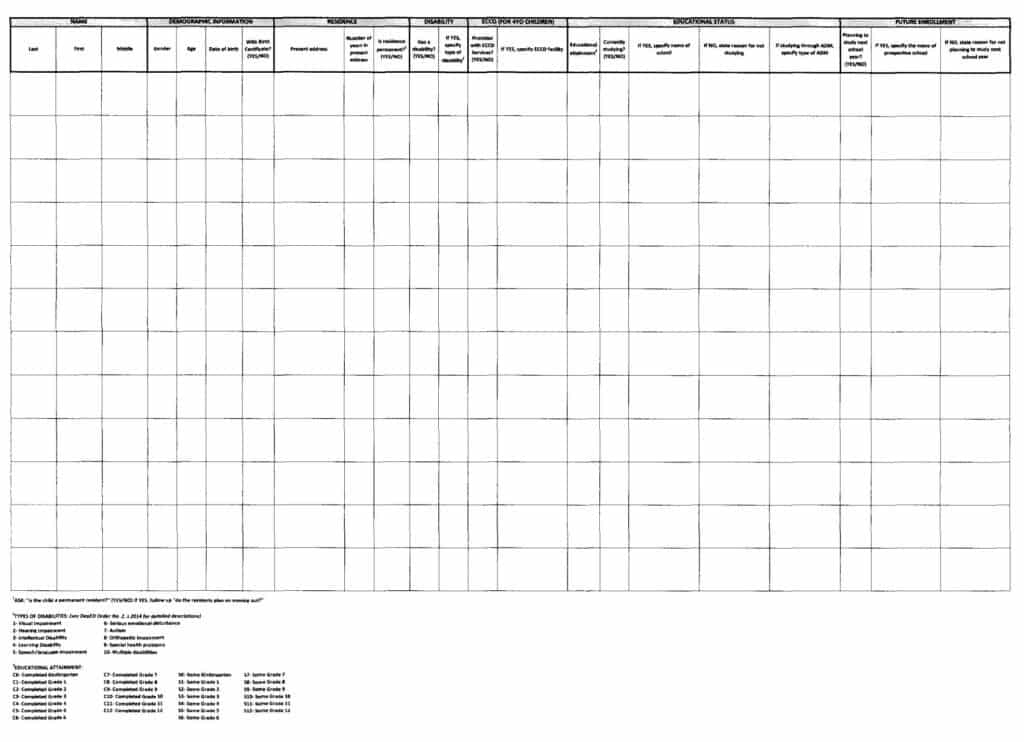
Before you go around your community to conduct your early registration activities, coordinate with the District or Division office and your barangay. If there are other schools in your barangay, coordinate with them as well.
Distribute this child mapping tool to your team of teachers and volunteers. They should fill this up as they move from house to house in the barangay. This will help you get important basic information on the status of 4-17 year old children in your community which you can use in school planning. You only need to cover your barangay unless majority of your students come from nearby communities, in which case, you need to conduct child mapping in those barangays as well. If there are no schools in a barangay, the District or Division office will initiate the child mapping in that area (following DO. No. 1, s. 2015).
Child mapping should be done at least every 3 years (preferably at the start of the SIP cycle), assuming that there are no major changes in the population of your community. After events causing major population changes (e.g. disasters), child mapping should be conducted to account for the children in your community.
After mapping, consolidate the data. You can encode it in the School-Community Data Template for easy reference. Share the data with your District and Division offices, barangay, and with nearby schools and communities.
Read: DepEd Basic Education Enrollment Policy
Table of Contents
LATEST 2018 CHILD MAPPING TOOL
Download DepEd Child Mapping Tool (Excel) – TeacherPH Facebook Group
TYPES OF DISABILITIES
A SPED-trained personnel, a health personnel, an NGO/PWD volunteer or regular teacher shall be assigned in each school to fill up the column Category of C/Y with Disability. They shall use the following for the screening and identification of children and youth with disabilities, who shall be registered in schools:
- Children/Youth with Visual Impairment. These children/youth have difficulty in seeing, even with the use of eye glasses for correction, adeversely affects their academic performance of the blind and low- vision learners. With the use of the E or Snellen chart, those who are blind have a visual acuity of 20/200 or 6/60 or less in the better eye, while those with low vision have a visual acuity of less than 20/60 or 6/18 in the better eye.
- Children/Youth with Hearing Impairment: These children/youth are deaf and hard-of-hearing. Those who are deaf have a severe hearing impairment that their hearing is non-functional for ordinary purposes in life, while those who are hard-of-hearing have a mild hearing impairment that allows learning without greater difficulty to communicate.
- Children/Youth with Intellectual Disability. These children/youth have significantly sub-average general intellectual functioning, existing concurrently with deficits in adaptive behavior.
d. Children /Youth with Learning Disability. These children/youth have a disorder in one or more of the basic psycological processes involved in understanding or using language, spoken or written, which may manifest in the an imperfect ability to listen, think, speak, read, write, spell, or do mathematical calculations. - Children/Youth with Speech/Language Impairment. These children/youth who have communication disorder such as stuttering, impaired articulation, a language impairment, or a voice impairment.
- Children/Youth with Serious Emotional Disturbance. These children/youth have a difficulty in building Satisfactory interpersonal relationships; respond inappropriately behaviorally or emotionally under normal cirscumstances; demonstrate pervasive mood of unhappiness; or have the tendency to develop physical symptoms of fears.
- Children/Youth with Autism. These children/youth have developmental disabilities that significantly affect verbal and non¬verbal communication and social interaction which are generally evident before age three.
- Children/Youth with Orthopedic Impairment. These children/ youth have physical disabilities, permanent or temporary, which can be paralysis, stiffness or lack of motor coordination of bones, muscles or joints, which results in the difficulty to move.
- Children/Youth with Special Health Problems. These children/ youth have limited strength, vitality, or alertness due to chronic or acute health problems.
- Children/Youth with Multiple Disabilities. These children/youth manifest two or more disabilities. Those who manifest two or more disabilities (mental retardation and blindness, etc.), the combination of which requires special accommodation for maximum learning.
May I know the difference between some grade 1 and completed kindergarten sir in the educational attainment code?